By Chris Lefkow
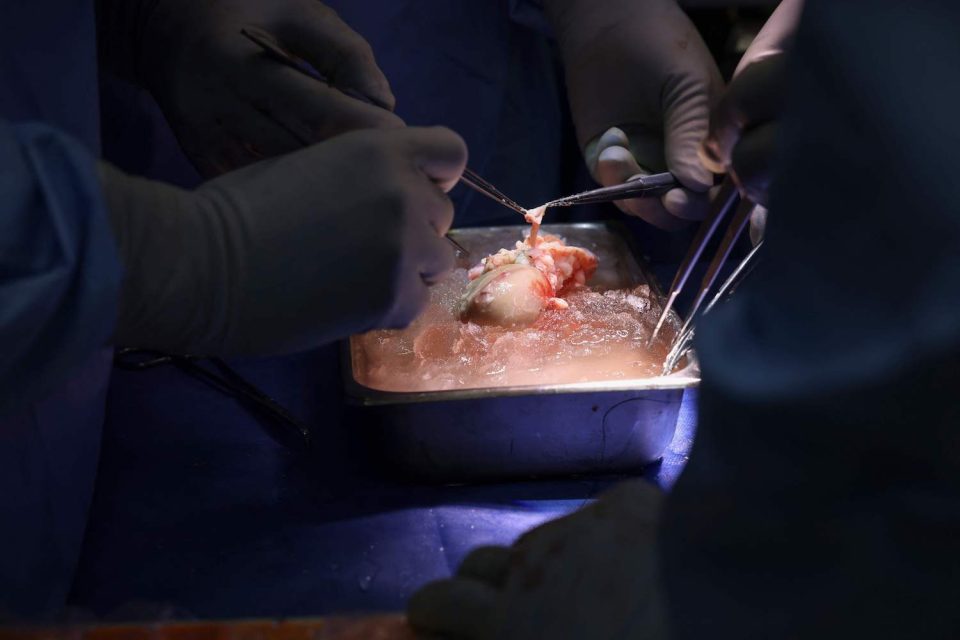
WASHINGTON, March 21, 2024 (AFP) – US surgeons have successfully transplanted a genetically modified pig kidney into a living patient for the first time, the hospital said Thursday, a procedure that could help address the chronic shortage of donor organs.
The four-hour operation was carried out on Saturday on a 62-year-old man suffering from end-stage kidney disease, Massachusetts General Hospital said.
“The procedure marks a major milestone in the quest to provide more readily available organs to patients,” the hospital known as Mass General, or MGH, said in a statement.
Organ shortages are a chronic problem around the world and the Boston hospital said there are more than 1,400 patients on the waiting list for a kidney transplant at MGH alone.
“Our hope is that this transplant approach will offer a lifeline to millions of patients worldwide who are suffering from kidney failure,” said Dr Tatsuo Kawai, a member of the team which carried out the ground-breaking operation.
The hospital said the pig kidney used for the transplant was provided by a Massachusetts biotech company called eGenesis and had been genetically-edited to remove harmful pig genes and add certain human genes.
“This represents a new frontier in medicine and demonstrates the potential of genome engineering to change the lives of millions of patients globally suffering from kidney failure,” said Mike Curtis, the chief executive officer of eGenesis.
The hospital said the patient, Richard Slayman of Weymouth, Massachusetts, “is recovering well at MGH and is expected to be discharged soon.”
He will be on a regimen of immunosuppressive drugs to ward off rejection of the pig kidney.
Slayman, who suffers from Type 2 diabetes and hypertension, had received a transplant of a human kidney in 2018, but it began to fail five years later and he has been on dialysis.
Slayman said he agreed to the pig kidney transplant as “not only as a way to help me, but a way to provide hope for the thousands of people who need a transplant to survive.”
- ‘Health equity’ –
Slayman is Black and the hospital said the procedure could be of particular benefit to ethnic minorities who suffer from high rates of kidney disease.
“This health disparity has been the target of many national policy initiatives for over 30 years, with only limited success,” said Slayman’s nephrologist Winfred Williams.
“An abundant supply of organs resulting from this technological advance may go far to finally achieve health equity and offer the best solution to kidney failure — a well-functioning kidney — to all patients in need,” Williams said.
The transplantation of organs from one species to another is a growing field known as xenotransplantation.
Pig kidneys had been transplanted previously into brain dead patients, but Slayman is the first living person to receive one.
Genetically modified pig hearts were transplanted recently into two patients at the University of Maryland, but both survived less than two months.
Mass General said the pigs used as organ donors were “grown in isolation under special conditions to prevent the pig from being exposed to infections that might harm the human recipient.”
“These special pigs have organs of similar size and function to human organs,” it said. “The genetic modifications of these pigs have also made them more compatible with humans.”
Mass General said the transplant was carried out under a policy known as “compassionate use” that allows patients with “serious or life-threatening conditions” to access experimental therapies not yet been approved by the Food and Drug Administration.







